Introduction
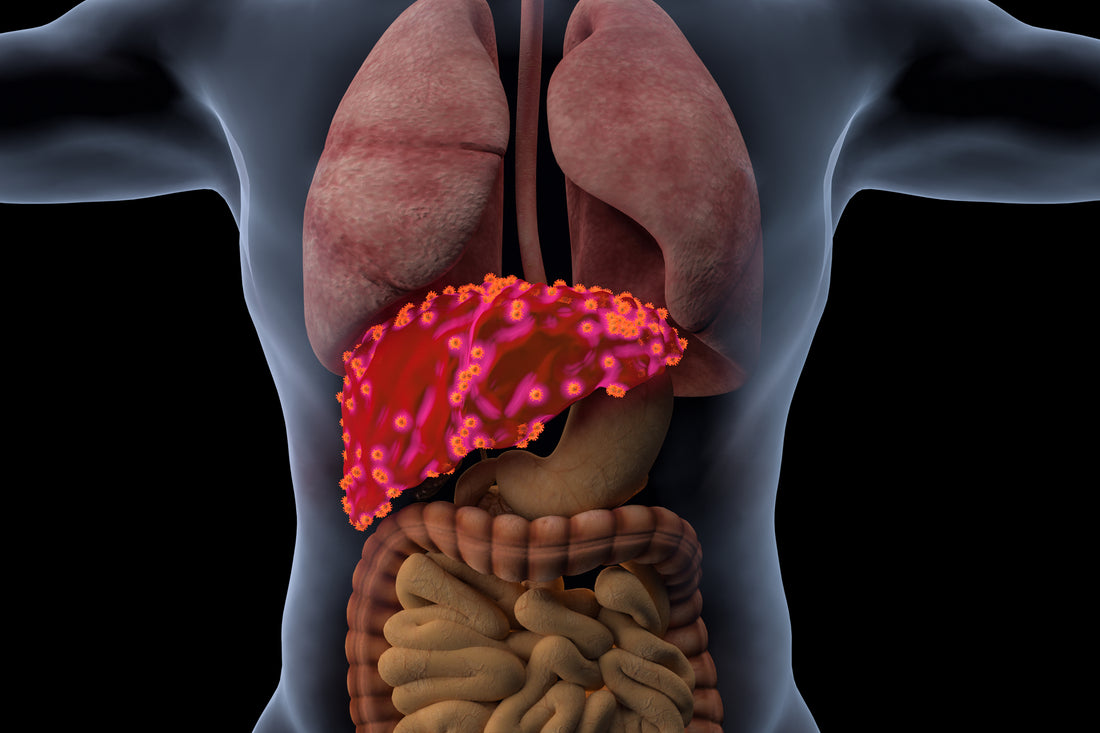
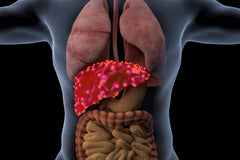
In simple terms, fatty liver is a complicated health issue, which indicates the excess amount of fat deposited in your liver. The major concern about fatty liver patients is they have to experience silent risk factors for this disease.
During the progression of fatty liver, most of patients usually experience zero symptoms. And at the severe phase of fatty liver, accumulated fats damage the liver cells and lead to liver dysfunction. Fatty liver is a chronic health issue that requires lifestyle modifications with restricted healthy diets.
What Is Fatty Liver?
Due to long-term fat accumulation in the liver, the liver becomes overweight and internal cells of the liver become affected by fat. So, fatty liver disease invites more critical health complications such as hepatitis and cirrhosis. Both of these health issues instigate life-threatening conditions.
Therefore, if your doctor recommends a specific diet for fatty liver and lifestyle changes, you should consider the doctor's suggestion. As much as you ignore doctors' recommendations, you eventually increase the risk factors of liver failure.
Types of Fatty Liver:
Based on these factors, fatty liver disease is categorized into two types:
1. What Is Alcoholic Fatty Liver?
Consumption of heavy alcohol causes extreme complications in internal liver functions. While alcohol enters your system, the body reacts with alcohol as a toxin, and the liver generates a biological process to flush it out. The liver generally executes multiple metabolism processes to synthesize fat, protein, and glucose. Similarly, when the liver executes alcohol metabolism, the byproducts remodel the ability of other metabolism processes by the liver. As a result, a decline in specific liver functions turns the liver into a fat-storing organ instead of a fat-synthesis organ. So, people highly addicted to alcohol can experience alcoholic fatty liver disease.
2. What Is Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver?
The progressive factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease do not cause serious health issues. So, the patients can not realize the risks at the initial stage of fatty liver. But, the long-term fat accumulation in the liver causes severe liver dysfunction. The entire stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver are categorized into four levels:
- Primary Fatty Liver (Steatosis)
- Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
NASH is quite a serious condition when patients face inflammation in the liver.
- Persistent Fatty Liver (Fibrosis)
Persistent fatty liver is a severe condition of fatty liver disease. In this stage, long-term inflammation in liver cells gradually causes tissue scarring around the liver, termed 'Fibrosis.' Till the Fibrosis stage, the liver manages its internal functions anyway.
- Severe Fatty Liver (Cirrhosis)
The severe stage of the fatty liver causes critical health issues. Despite long-term inflammation, in the primary stages of NAFLD, if patients do not adopt the doctor's recommended diet & lifestyle changes, they face serious health issues. The severity of inflammation leads to liver shrinkage.
In this stage, the lumpy & scarred tissues in the liver cause liver failure. While people experience the first two levels of fatty liver, they should be careful about their daily diet & lifestyle.
From the initial conditions of nonalcoholic fatty liver, developing severe conditions such as - Fibrosis & Cirrhosis takes years. Therefore, people should not ignore inflammation in the liver as it leads to dangerous & life-threatening liver cancer.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver:
Who Are Prone To Fatty Liver Disease?
The following points describe whether you have enough chances to develop critical fatty liver disease.
- People who are prone to chronic obesity often experience nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- If you have high diabetes mellitus, you are prone to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Patients with high blood pressure & high cholesterol are also can be victims of fatty liver disease.
Major Signs of Fatty Liver:
At the start of fat accumulation in the liver, most patients have zero complications. But, at a certain level, fatty liver patients face critical health issues such as:
- Swelling in the liver.
- Fatty liver patients often feel uncanny fullness in the right side of the upper abdomen.
- Fatty liver disease can cause specific health issues, such as Jaundice, which is detected by yellowish skin, eyes, and a high amount of bilirubin.
- Abdominal pain is also a major sign of fatty liver.
- Fatigue or extreme tiredness is also a major symptom of fatty liver.
Causes of Fatty Liver:
What Factors Leads To Alcoholic Fatty Liver?
- Liver Enzymes Break Down Ethanol
People, who are habituated to consuming alcohol on an everyday basis, often face the risk factors of alcoholic fatty liver. Generally, while the body receives large amounts of alcohol within a certain period or regular basis, the liver breaks down the alcohol solids by enzymes to flush it out from the body. This biological process is termed as 'Alcohol Metabolism.'
- Alcohol Metabolism Affects Internal Liver Functions
So, people who drink alcohol daily face internal liver dysfunction. Due to harmful toxin generation in the liver, alcohol metabolism impairs lipid metabolism, instigates inflammatory reactions, and increases the risk factors of fibrosis.
- Alcohol Metabolism Affects The Process of Fat Oxidation
Recent studies claim additional effects of alcohol metabolism impair the process of Fat Oxidation(when with the help of healthy mitochondria, the body breaks down fat contents - triglycerides into tiny molecules - glycerol & fatty acid, which supply consistent energy ).
Regular or excessive alcohol consumption alters mitochondria functions. As a result, the cycle of citric acid activities interrupts the fat oxidation of fatty acid formation. So, due to daily alcohol consumption, heavy ethanol properties inhibit the fat oxidation of fatty acid formation.
So, excess alcohol in the liver leads to mitochondria dysfunction, which decreases the rate of fat synthesis. Then triglyceride can not be converted into fatty acid for fuel or energy in the body. And thus, in the body of alcoholic people, fat or triglyceride is accumulated in the liver & adipose tissues and causes fatty liver disease.
- Ethanol Properties Affect Lipid Metabolism
The liver acts like a 'Buffering Organ' in the human body. It plays essential roles in carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism & fat oxidation. Through all these biological processes, the liver synthesizes carbohydrates, protein, cholesterol, and fat and generates byproducts to fuel the body's mechanisms, then stores the excess leftovers as byproducts.
Due to excess alcohol in the liver, when lipid metabolism is affected, the liver can not produce constituents, bile's, which play key roles in absorbing fat. As a result, the liver fails to digest fats & convert them into fuel for the body efficiently. Therefore, alcoholic people experience excess fat accumulation in the liver, medically termed 'Fatty Liver Disease.
What Factors Cause Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver?
- Obesity Affects Metabolic Pathway & Causes Fatty Liver:
In general, adipose tissue is an integrated & complex endocrine organ that essentially produces metabolic hormones(Metabolites, which are known as Adipokines) such as - leptin, apelin, resistin, visfatin, adiponectin, and so much more. All these hormones play key roles in the modulation of metabolic processes in the human body.
Adipose tissue communicates with the central nervous system, which regulates energy distribution throughout the body. In brief, adipose tissue plays a critical role in systemic energy homeostasis. On the other hand, adipose tissue is the major caloric reservoir of the body. On one side, Adipokines regulate the signals received from CNS(Central Nervous System).
As well as Adipokines play a major role in defining nutritional status. Obesity is a multifactorial trait that increases the mass in fatty tissues. So, in overweight conditions, excess mass in adipose tissue crucially alters the number & size of adipocytes and also changes the proportion of adipokine secretion, leading to the death of adipocytes.
So, there is no doubt that obesity remodels the functions of adipose tissue. And finally, a lack of metabolic regulations triggers inflammatory responses. Thus, due to obesity-driven metabolic disorders, uncontrolled inflammatory responses lead to disorders in fat synthesis. And obese people face fatty liver disease.
- High Diabetic Mellitus Triggers Fatty Liver Disease?
The underlying factor behind diabetes, such as insulin resistance, impaired carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, and protein metabolism. Moreover, in diabetic conditions, adipose tissue becomes insulin sensitive.
As a result, due to insufficient fatty acid oxidation, adipose tissue increases the delivery of fatty acids, which stimulates De Novo lipogenesis. Besides, due to insulin resistance, hepatic fat accumulates in the liver when adipose tissue boosts the fatty acid supply. As a result, diabetic patients face the complications of fatty liver. Therefore, underlying diabetes factors cause nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
- High Triglyceride Level Causes Fatty Liver:
Unhealthy diets lead to overnutrition, which is responsible for heightening triglyceride levels. While triglyceride level crosses the limits of 1500 MG/DL, it hinders Hepatic Fatty Acid Metabolism. Fatty Acid Metabolism is a multifactorial process executed in the liver in four phases - Dehydrogenation, Hydration, Oxidation & Thiolysis.
All the phases are essential for fat synthesis, which releases fatty acids to serve energy to the different aerobic tissues. Due to overnutrition, while high amounts of triglyceride start to decline Fatty Acid Metabolism, the liver fails to turn fat into energy. And due to the accumulation of excess fat, people experience fatty liver disease.
Diagnosis Of Fatty Liver:
- How Is Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diagnosed?
When patients go to doctors with persistent signs of discomfort in their right upper abdomen, fatigue, or Jaundice issues, doctors recommend some lab tests after routine checkups. If the imaging test reports show an enlarged liver or a high liver enzyme level, healthcare professionals or doctors suspect NAFLD (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver).
Based on the basic lab test reports, doctors recommend further specific blood tests as they need to recognize the factors behind high levels of liver enzymes. In different cases, doctors or healthcare professionals go ahead for sensitive & intensive imaging labs tests such as MRI or CT scan to examine your liver.
In severe conditions of liver dysfunction, another method to detect Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver is Liver Biopsy. As it is an intensive diagnosis method, during Liver Biopsy, your healthcare professional inserts a tiny needle to collect liver tissue, and after analysis, they reach the verdict on how much fat is deposited in the liver cells or describe the evidence of permanent scarring in liver cells.
- How is Alcoholic Fatty Liver Detected?
Doctors recommend LFT(Liver Function Test) when they suspect internal damage in the liver due to alcohol. Through Liver Function Tests, healthcare professionals find high levels of AST (Aspartate Aminotransferase), which reacts with ALT (Alanine Aminotransferase). It means that the ALT level is heightened due to excess alcohol consumption, boosting the risk factors of liver dysfunction.
Treatment of Fatty Liver:
Is Ayurveda Effective In Fatty Liver Treatment?
Ayurveda follows ancient formulations to manage the lifestyle and rejuvenate health. So, the following Ayurveda treatments work effectively to cure fatty liver disease:
- Triphala
Triphala is a proactive combination of three fruits - Haritaki, Amla, Bibhitaki. The blend of these triple ingredients offers outstanding cleansing effects, which promote balance in liver functions. So, due to having an extreme level of detoxification power, Triphala is highly effective in curing liver dysfunction.
- Shankhapushpi
Obesity-driven impaired metabolism expands the adipose tissue mass. During lipolysis, the extended adipose tissue produces NEFA (Non-esterified Fatty Acid). The elevated level of NEFA causes a decline in glucose metabolism in the liver and leads to fatty liver disease.
Research has demonstrated that the Ethanolic extract of Shankhapuspi effectively decreases the level of NEFA (Non-esterified Fatty Acid). So, as an Ayurvedic herb - Shankhapuspi effectively fights the multifactorial internal risk factors of fatty liver.
- Gaggulu
Lots of Ayurvedic medicine is prepared with a moderate amount of Resin extract collected from the Guggulu tree. The specific formulation of Guggulu Ayurvedic medicine plays a vital role in improving metabolic disorders in the liver. So, fatty liver patients get effective results with Gaggulu ayurvedic medicine.
- Milk Thistle
Milk Thistle is a proven Ayurvedic medicine that effectively treats both alcoholic fatty liver & nonalcoholic fatty liver complications.
The Ayurvedic formulation of Milk Thistle contains Silymarin, a powerful antioxidant that slows down the inflammatory reactions in the stage of Steatosis. So, fatty liver patients get soothing results with Milk Thistle solutions, while they feel uncomfortable due to Steatosis swelling in the liver.
What Are The Effective Home Remedies In Fatty Liver?
Physical Activity Is Must:
Fatty liver patients should pay attention to moderate amounts of regular exercise. You can enlist very simple works in your daily routine as a home remedy for fatty liver.
Regular general activity, such as playing with kids, opting for stairs, avoiding elevators, walking with pets, and visiting the grocery store on foot. All these simple matters turn your sedentary lifestyle into mobility. And if you become habituated to walking for 30 minutes a day a week, it will reduce the risk factors associated with NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease).
Dietary Changes Are Required:
Sugar intake is highly responsible for the fat buildup in your liver. So, all processed food, including cookies, cakes, pies, pastries, doughnuts, candy, ice cream, sweetened dairy products, and flavored yogurts, which contain Maltose, Fructose, and Sucrose, is strictly prohibited for fatty liver patients
Mediterranean Diet Is Essential :
Research says the Mediterranean diet is helpful for quick recovery from fatty liver complications. So, keep the following foods in your regular diet as you can reduce fatty liver complications:
Olive Oil - If the fatty liver patients consume half-cup of first-pressed, unrefined, extra-virgin olive oil with half lemon juice or grapefruit juice during bedtime, it works best for fatty liver recovery.
Garlic - Garlic is loaded with a specific mineral - Selenium, which plays a vital role in detoxifying your liver. Moreover, Garlic flushes out toxins from the body by activating liver enzymes. The most significant fact of Garlic is it contains Allicin, a sulfur compound. If fatty liver patients intake uncooked Garlic, the liver produces Glutathione during the digestion of Allicin. And research says Glutathione flashes out the Hepatotoxin from the liver.
Almonds - Almonds are loaded with Vitamin -E, which improves liver health. As a powerful antioxidant, Vitamin- E combats free radicals & also protects liver cells from harmful toxins.
Cruciferous Veggies- Research claims that patients with mild to severe symptoms of fatty liver should keep cruciferous vegetables such as - Kale, Cabbage, Brussels Sprouts & Cauliflower in their everyday diet. All these veggies contain Glutathione. Glutathione is such a peptide, which is essential in eliminating drugs and pollutants from the body. So, Glutathione is also a powerful antioxidant, which cleanses the Hepatotoxin, which is responsible for fatty liver.
Amino Acid & Sulfur-Rich Food: Celery & Mushrooms are the richest sources of Amino acids. Leafy green vegetables & cruciferous vegetables are loaded with sulfur. While the liver digests the bio-compounds - amino acid & sulfur, which come from specific foods, Glutathione is produced by the liver. Glutathione is required to eliminate the Hepatotoxin, the major culprit that causes fatty liver diseases. So, fatty liver patients should add fresh vegetables, and specific whole grains such as - quinoa to their diet, as they are the richest sources of natural Sulfur & Amino acids.
Green Tea: Research claims Matcha Green Tea is highly powerful in inhibiting obesity-driven metabolic syndrome. So, if you intake Matcha Green tea daily, it will effectively inhibit the deposit of hepatic lipid & visceral fat in liver cells. So, patients, who face fatty liver complications, should consume green tea to prevent liver dysfunction.
Coffee: The presence of caffeine & antioxidants in coffee promotes liver health. Besides, polyphenols in coffee act as anti-inflammatory properties. So, while you intake coffee, it prevents inflammations in the liver. Moreover, while the liver digests caffeine, it produces a byproduct - Paraxanthine. Paraxanthine is essential in slowing down the development of scar tissue in the Fibrosis stage of fatty liver.